As countries return to the lunar surface, there is an instrument that can detect water on the moon
Learn more about the Instrument which can detect water on the moon.
Thursday, 8th July 2021
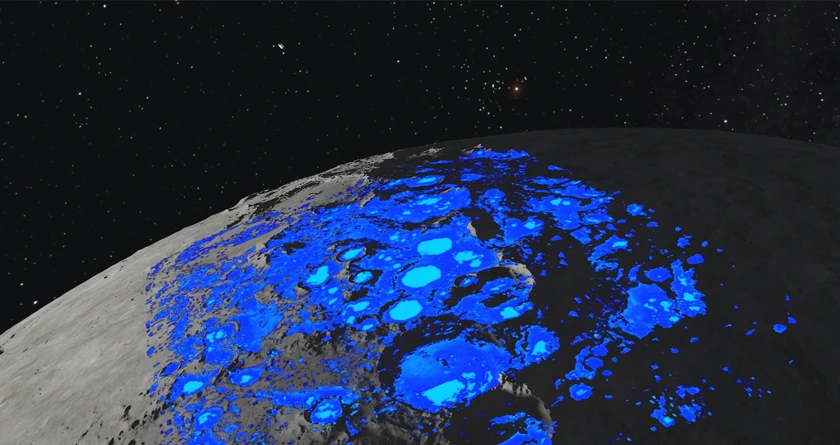
As countries return to the moon, this time they plan to stay and establish a long-term presence. One of the most important explorations will be to find water on the surface of the moon. A team of scientists dedicated to finding the occurrence and behavior of water on Earth's natural satellites has designed an instrument that can detect water molecules from the surface.
A team from the Open University (OU) and RAL Space assembled an outer mass spectrometer (EMS), called the "heart of the lunar sensor", which will study the abundance of water and ice needed for the next lunar mission. The spectrometer is part of the PITMS instrument and will be delivered to NASA later this year for launch to the Moon.
As part of NASA's ambitious Artemis mission, the instrument will reach the Moon Decades after the Apollo mission, the first female and next male astronauts will return to the lunar surface.
"The instrument will measure the water and other molecules in the very thin atmosphere of the moon on a lunar calendar day, testing the emerging concept of the lunar water cycle. The instrument will also test some of the detection techniques that OU will use in subsequent missions." The statement said.
HOW DOES IT DETECT WATER ON THE MOON?
According to ESA, the instrument allows researchers to identify and quantify samples of atoms and molecules in the gas through chemical analysis. The moon molecules entering the sensor are bombarded by electrons, producing ions, which are stored in an electric field. These ions are then released into the detector, which recognizes and quantifies their chemical composition.
Also Read: Far away from the earth, this 20-year experiment explores an invisible world living among us.
This instrument will measure the water and other molecules in the very thin atmosphere of the moon throughout the lunar calendar to study the concept of the moon's "water cycle". The instrument will be part of the lunar lander, which will reach the moon in 2021 in NASA's celestial robot mission in the Valles Mortis area.
The team previously designed a sensor to identify lunar volatiles. The ion trap mass spectrometer (ITMS) is a part of an instrument that can detect lunar volatiles from the moon’s extremely thin atmosphere and lunar soil.
WHY ARE WE GOING BACK TO THE MOON?
The exploration of the moon, which has been neglected since the end of the Apollo mission in the 20th century, is accelerating again as the missions of the United States, China, Russia, and India go to the surface. boundary. Interplanetary exploration. Although the establishment of a base as part of a stopover during a trip to Mars has been on the agenda, another important aspect is that rare metals on the earth may exist on the moon, which can be used to develop new technologies.
"The materials found on the surface of the moon can provide valuable resources to support future exploration missions. This is especially true near the poles of the moon, where extreme cold conditions can capture water ice. These resources can enable sustainable space exploration, but there are still many unknowns," ESA said.
The News Talkie Bureau
Source:
India Today