A tempest greater than whole Earth: Wind speed in Jupiter's Great Red Spot accelerating, blowing at more than 640 kmph
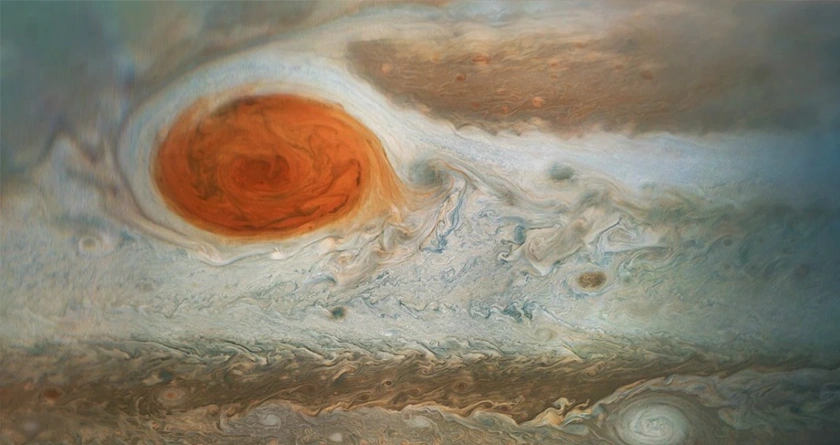
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot.
Wednesday, 29th September 2021
Jupiter has consistently been the focal point of interest for space experts, nonetheless, it's not simply the amazing size of this planet that stands out however wonders on a superficial level too. One such is the Great Red Spot, a gigantic tempest that can be seen barreling on the outer layer of the greatest planet in the planetary group.
Groundbreaking perceptions from the Hubble Space Telescope show that the speed of this tempest is expanding. The telescope has radiated back information demonstrating that the breezes in the furthest "path" of Jupiter's Great Red Spot are speeding up. The most recent tempest reports show that the normal breeze speed just inside the limits of the tempest, known as a fast ring, has expanded by up to 8 percent from 2009 to 2020.
In the meantime, the breezes close to the red spot's deepest district are moving essentially more leisurely. The Great Red Spot has been noticed seething in the world for more than 150 years as the blood red-hued mists turn counterclockwise at speeds that surpass 600 kilometers each hour.
The vortex of this tempest is greater than Earth.
"At the point when I at first saw the outcomes, I asked 'Does this bode well?' No one has at any point seen this previously. In any case, this is something no one but Hubble can do. Hubble's life span and progressing perceptions make this disclosure conceivable," said Michael Wong of the University of California, Berkeley, who drove the examination.
WHAT IS THE GREAT RED SPOT?
The Great Red Spot is the lord of tempests in our nearby planetary group. A new flyby of the Juno shuttle assisted researchers with verifying that the tempest's underlying foundations stretch out something like 320 kilometers into Jupiter's air. For correlation, a run-of-the-mill typhoon on Earth just reaches out around 15 kilometers.
Nasa says that the Great Red Spot is an upwelling of material from Jupiter's inside. Stargazers have noticed that it is shriveling and turning out to be more roundabout than oval in perceptions crossing over a century. The current measurement is more than 16,000 kilometers across, implying that Earth could in any case fit inside it.
The red band above and to one side (upper east) of the Great Red Spot contains mists moving toward the west and around the north of the monster whirlwind. The white mists to one side (southwest) of the tempest are moving toward the east toward the south of the spot.
TRACKING STORMS
Following tempests on Earth is excessively difficult, in any case, storm chasers, Earth-circling satellites, and planes track significant tempests in the world. Yet, to follow a comparable occasion on another planet, the main conceivable instrument is the Hubble Space Telescope. Nasa said that the flying observatory is the main telescope that has the sort of fleeting inclusion and spatial goal that can catch Jupiter's breezes in this detail."
"We're discussing such a little change that in the event that you didn't have eleven years of Hubble information, we wouldn't realize it occurred. With Hubble we have the accuracy we need to detect a pattern," said Amy Simon of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, who added to the examination. As indicated by specialists, the adjustment of wind speeds they have estimated with the Hubble adds up to under 2.5 kilometers each hour each Earth year.
Scientists concentrated on information traversing back to twenty years to discover that the normal breeze speed in the Great Red Spot has been somewhat expanding. Investigation of a two-dimensional breeze map discovered unexpected changes in 2017 when there was a significant convective tempest close by. Analysts then, at that point, followed tens to countless breeze vectors (bearings and paces) each time Jupiter was seen by Hubble.
WHAT DOES THE INCREASE IN WIND SPEED MEAN?
While the Hubble Telescope affirms that the breeze speed in the Great Red Spot has expanded, it is hard to anticipate its effect in the world since cosmologists can not see the surface.
"That is difficult to analyze since Hubble can't see the lower part of the tempest well overall. Anything beneath the cloud tops is undetectable in the information," clarified Wong. "In any case, a fascinating piece of information can assist us with getting what's energizing the Great Red Spot and how it's keeping up with energy." There's still a ton of work to do to completely get it.
The News Talkie Bureau
Source:
IndiaToday